Larry Summers crystallised an important development and question in a recent speech given at the IMF research conference: Has the world economy entered a period of ‘secular stagnation’? The slow recovery in the US since the Global Crisis is his starting point and he argues that secular stagnation could also retrospectively explain features of previous decades such as low inflation. Summers thereby picked up an old term from Alvin Hanson (1939), who used it in the Presidential Address of the American Economic Association in 1938. Back then, Hanson focused on the importance of (public) investment expenditure to achieve full employment. His argument was that for such investment to happen, the economy needs new inventions, the discovery of new territory and new resources, and finally population growth.
Summers’ argument is centred on the fact that inflation rates have been falling in the past two decades and have been mostly lower than expected. Has there been a permanent fall in the equilibrium real interest rates? Do our economies need real interest rates of -2% or -3% to generate enough demand to achieve full employment? Is the fact that inflation rates were so low and even falling over the last decades really a sign that the global economy was suffering from a permanent demand weakness? Was there really no demand excess?
Olivier Blanchard (2013) has written a VoxEU column summarising and drawing lessons from the recent IMF conference at which Larry Summers spoke. One lesson is that it paid off to have kept one’s fiscal house in order prior to the crisis. He then focuses on how to macro-manage a liquidity trap. In fact, if one agrees with his assessment that the effects of unconventional monetary policy are “very limited and uncertain”, then one can come rapidly to his conclusion that it would be advisable to have higher inflation rates in normal times, which makes it possible to drive down nominal interest rates more in a crisis so that real interest rates fall even further. Krugman (2013a) goes one step further, even arguing that the new normal may be a permanent liquidity trap, and it would therefore not be advisable to have low inflation rates in the Eurozone (Krugman 2013b)
Three central policy measures to deal with secular stagnation
While I see the merits of the arguments of Krugman, Blanchard and Summers, I am worried that too little thinking is being put into the actual real economic drivers of secular stagnation and what could be done about them. Let me organise my thinking around three central points.
First, prior to the crisis, the global economy generated just enough demand to achieve reasonable employment rates thanks to significant bubbles in a number of major economies, excess borrowing by low-income households, high corporate borrowing, and/or unsustainable fiscal policies to balance the large amount of global savings. With the erupting crisis, high household, corporate and government borrowing and the house-price bubbles became visible as unsustainable sources of global demand. So would the answer to secular stagnation really have been more demand? Or put differently, how could one have achieved higher inflation rates prior to the crisis, as Blanchard suggested, without creating even more bubble-like phenomena? Isn’t the suggestion to solve the liquidity trap problem by running higher inflation rates prior to the crisis an attempt to cure the problem with the problem itself? If there is an insufficiency of demand even in normal times, this problem would need to be addressed with structural policies. The answer can hardly be more bubbles so that inflation rates go up. Using monetary policy to drive the real interest rate permanently to low, or perhaps even negative, rates is difficult and can create significant distortions in the economy.
This point can be illustrated by the US example. While monetary policy has been very supportive and has helped avoid a slide into deflation during the crisis, arguably before the crisis it contributed to the build-up of many of the problems in the US economy. The massive bubbles that resulted from the combination of lax monetary policy and an inadequate financial regulatory system should certainly be considered a problem, not a solution. A perhaps more important part of the solution to the current problem has been the acceptance of structural policies that are more conducive to a recovery; the US recovery has been helped by very significant debt reductions in the household sector thanks to non-recourse mortgages and the like. More importantly, the banking system has been cleaned up relatively quickly, which also helped the recovery.
Turning to the Eurozone, I would advise against changing the ECB’s inflation target of close to, but below, 2% for two reasons. First, such a step would severely undermine trust in a young institution whose actions are still criticised in some countries of the EU’s young monetary union. It would constitute a breach of the contract under which Germany subscribed to the monetary union. Second, changing the target under current circumstances would be largely ineffective; the current target will not be achieved in the relevant time horizon, and a higher target would only increase this gap.
Second, like Hansen, I believe in the importance of the structural factors that actually provide investment opportunities. The overall lesson of secular stagnation, as outlined by Larry Summers, seems to go in a different direction from monetary policy that, in normal times, can hardly help address an equilibrium negative real interest rate without risking major bubbles and unsustainable borrowing, as the European and US experiences suggest. The fundamental question is why has the equilibrium interest rate been falling globally and the global economy entered ‘secular stagnation’. Is it global demographics? Is it the lack of good investment opportunities? Is it the fact that we lack new places that can be ‘conquered’?
Certainly, population growth is starting to fall in many countries, especially in the more advanced economies. Yet, the global population is still increasing. This would suggest that globally, there should still be ample investment opportunities if framework conditions are put right. This is where the role of the integration of Asian and African economies into the global economy becomes central. More than half of the world’s population is concentrated in a small circle in Asia, including China and India. The more they are integrated into the global economy, the more they should increase global demand, and the more opportunities for profitable investment should exist. To achieve this, a well-functioning financial system is critical. It would need to prevent excessive risk-taking while channelling savings to the right countries and deployments. Clearly, critical questions are if and how saving and investment patterns will change in Asia. How sustainably capital accounts are opened up will also be critical.
The Eurozone also provides important evidence that structural policies that allow for capital to be channelled into productive uses, that allow new innovations to emerge, and that allow for new inventions are critical. Prior to the crisis, many thought that the Eurozone had solved the secular stagnation problem and had actually provided the right framework conditions for more investment. The capital flows in the European periphery were praised for proving that capital would flow ‘downhill’, where its marginal productivity is still highest. Unfortunately, the reality turned out to be much less rosy. Instead of being used productively, much of the capital flows went into consumption spending, including on housing. As in the US and UK, increasing house prices initiated a financial accelerator model in which more and more borrowing followed, thereby driving a consumption boom.
The European experience underlines the importance of structural reforms that allow for proper business opportunities and innovation. The downhill capital flows are welcome in principle, but they only contribute to sustainable growth if they flow into an environment in which they can drive investment, as outlined by Hansen. In the European case, part of the problem was that the financial system did not properly steer capital flows into those productive uses. The regulatory and supervisory system of Europe’s monetary union was not properly developed, risk became too concentrated and moral hazard was prevalent. The creation of Europe’s banking union, while incomplete, is certainly a step in the right direction to solve this problem. But I am also convinced that Europe should be able to create much better investment opportunities to solve its stagnation. For this, reforms that reduce administrative burdens, improve education systems and create better conditions for R&D are central.
Turning to Japan, the importance of structural reforms also becomes apparent. Since the election of Shinzo Abe as prime minister, Japan has embarked on a QE programme on an unprecedented scale. The effect has been a much weaker yen, together with an increase in inflation. This was a welcome policy development. Yet, one year later, it also becomes clear that a strategy based on a weaker yen to increase exports as the only anti-deflation strategy cannot work forever. To return to growth and inflation, the third arrow of Abenomics matters equally: improving investment conditions, creating new business opportunities, increasing competition in the economy, and deepening trade integration.
Third, how shall macroeconomic policies deal with the liquidity trap, low inflation and insufficient demand problem in the Eurozone of today? Six years on from the beginning of the crisis, growth remains sluggish and inflation rates are low or falling. The Eurozone is still at risk of falling into deflation. Eurozone core inflation rates, i.e. inflation rates excluding volatile energy and food prices, have been falling since late 2011. Inflation expectations two years ahead are hardly above 1%, and even at the five-year horizon the market-determined inflation forecast is 1.19%. This has consequences. Lower-than-expected inflation redistributes wealth from debtors to creditors and increases the burden of the debtors. Thus, disinflation in the Eurozone undermines private and public debt sustainability, in particular in the periphery where the debt overhang is greatest. It is therefore a real risk for the Eurozone as a whole and should be addressed.
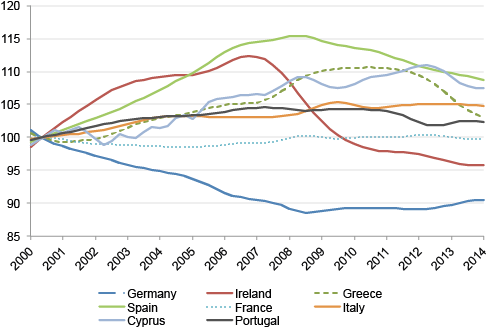
I see a role for both monetary and fiscal policy in helping to overcome this low growth-low inflation environment. Turning first to monetary policy, it has to deal with two central problems in the Eurozone. The first is that monetary policy should not undermine the ongoing relative price adjustment process between the Eurozone periphery and core (see Figure 1). A monetary policy measure that would increase inflation in the periphery would only undermine the restoration to health of the Eurozone economy. Instead, the policy measure should ensure inflation rates are increased in Germany as well as in the periphery. Ideally, the German inflation rate should move well above the 2% target that the ECB has set for the Eurozone as a whole. The second concern in the Eurozone right now is that the process of the banking sector clean-up is unfinished. The ECB would certainly like to avoid preventing a bank restructuring with monetary policy measures that would overly distort prices.
Figure 1: Real effective exchange rate versus EZ18
Note: The real effective exchange rate vs EZ18 aims to assess a country’s price or cost competitiveness relative to the currency area as a whole. It corresponds to the nominal effective exchange rate deflated by the GDP deflator.
Source: DG ECFIN – E4.
In Claeys et al. (2014), we have argued that a quantitative easing (QE) programme focused on the purchase of ESM/EFSF/EIB/EC bonds, corporate bonds and ABS would overcome those constraints and help to increase inflation via a portfolio-rebalancing effect and a weaker exchange rate. The recent decision by the ECB (2014) – while a welcome form of monetary and credit easing – is unlikely to be enough to push demand and inflation upwards. I am thus not quite as negative on QE as Olivier Blanchard and also believe that the Japanese experience shows that a large monetary policy measure can be part of the solution, even if the nominal interest rate is already at the zero lower bound.
But fiscal policy will also have to play a larger role. One of the big problems in the Eurozone has been the weakness in public investment in recent years, in contrast to the US where public investment actually increased. Much the weakness in public investment needs to be solved by more public investment in Germany. More European-level investment in European public goods, such as new and better energy and digital networks, should also be undertaken. This brings us back to the work by Hansen: public investment and new investment opportunities are needed to address secular stagnation.
References:
Blanchard, O (2013), “Monetary policy will never be the same”, VoxEU.org, 27 November 2013
Claeys, D, Z Darvas, S Merler and G B Wolff (2014), “Addressing weak inflation: The ECB’s shopping list”, Bruegel policy contribution.
ECB (2014), ECB press conference, 5 June.
Hansen, A (1939), “Economic progress and declining population growth”, American Economic Review 29(1).
King, S (2013), “There is no easy escape from secular stagnation”, FT.com blog, 25 Nov
Krugman, P (2013a), “Three charts on secular stagnation”, The New York Times blog, 7 May.
Krugman, Paul (2013b), “Secular stagnation in the euro area”, The New York Times blog, 17 May
Summers, Lawrence H (2013), "Crises Yesterday and Today", speech at the 14th Jacques Polak Annual Research Conference, Washington, DC, 7 November.